Understanding OOP Concepts: OOP, Class & Object
In this article, I’m going to talk about OPP, Class & Object. OOP provides a clear modular structure for programs. Let’s try to get the basic idea:
Table of Contents
What is OOP?
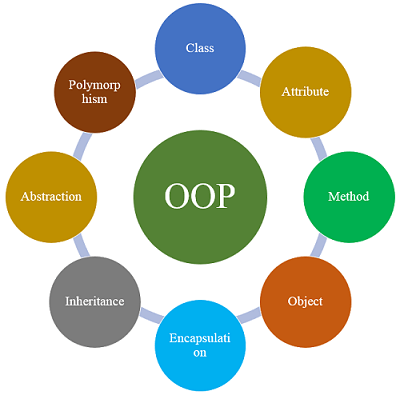
Object-oriented programming is a programming methodology constructed around objects. OOP is associated with concepts such as class, object, Inheritance, Encapsulation, Abstraction, Polymorphism etc.
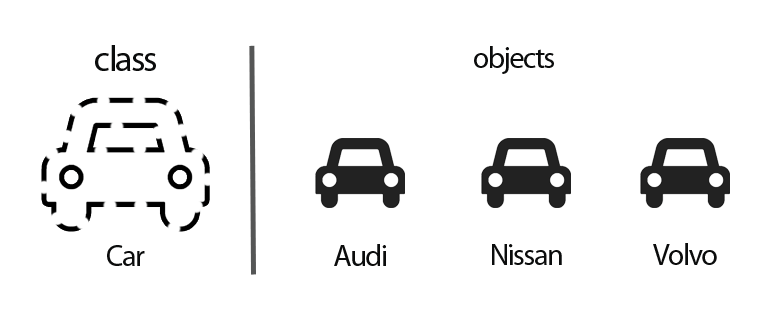
Before going to understand class & object, let’s have a look at the following figure:
Understanding Class
Class is a blueprint or template that defines the data and behavior of a type. It is a collection of properties and methods.
According to Figure 2, Car is a class. In the Car class, we may define the car brand, model etc. These are called properties/states/attributes. We’ll learn more about properties in the next article.
Note: When a class is defined, no memory is allocated.
Understanding Object
An object can be considered as an instance of a Class. It is a bundle of some characteristics and behavior.
According to Figure 2, Audi is an object of the Car class.
Note: When an object is created, memory is allocated.
Example in Java
This is the Car class in Java:
public class Car {
// properties, methods, etc.
}and this is the object of Car:
Car audi = new Car();Example in PHP
Let’s write the Car class and Audi object in PHP:
// class
class Car {
// properties, methods, etc.
}
// object
$audi = new Car ();I’ll explain the properties and methods in the next article in detail.
Md Obydullah
Software Engineer | Ethical Hacker & Cybersecurity...
Md Obydullah is a software engineer and full stack developer specialist at Laravel, Django, Vue.js, Node.js, Android, Linux Server, and Ethichal Hacking.