Build Node.js RESTful API CRUD with Express.js and MongoDB
In this guide, I’m going to make a simple Node.js CRUD API application with Express and MongoDB. I’ll create a products table and will implement the following APIs methods:
| Method | URL | Action |
|---|---|---|
| POST | products/create | create new product |
| GET | products | retrieve all products |
| GET | products/id | retrieve product where id=id |
| PUT | products/update/id | update product where id=id |
| DELETE | products/delete/id | delete product where id=id |
Table of Contents
- Create Project and Install Dependencies
- Connect to MongoDB
- Create Product Model
- Create Product Controller
- Register Product Routes
- The Overview
- Run and See Output
Step 1 : Create Project and Install Dependencies
Install the Express application generator globally using this command if you didn’t install:
# with NPX command (available in Node.js 8.2.0)
npx express-generator
# with NPM command
npm install -g express-generator
Now go to the project folder and create an express project called ‘crud-api-mongodb‘:
# create project
express --view=ejs nodejs-api-crud-mongodb
# go to the project folder:
cd nodejs-api-crud-mongodbWe need to install the mongoose package for MongoDB:
npm install --save mongooseStep 2 : Connect to MongoDB
In the root of the project folder, create a folder called ‘lib‘. Under lib folder make a file named ‘db.js‘. Open the newly created db.js file and paste the below code:
// Set up mongoose connection
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
let database_url = 'mongodb://localhost:27017/testdb';
// Connecting to the database
mongoose.connect(database_url, {
keepAlive: true,
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
useFindAndModify: false,
}).then(() => {
console.log("Successfully connected to the database");
}).catch(err => {
console.log('Could not connect to the database. Exiting now...', err);
process.exit();
});
module.exports = mongoose.connection;In the database_url variable, enter your database URL. You can set remote URL too. I’ve set the localhost URL. In the last of the database_url, the testdb is the database name.
Now open app.js file and add this line to include the database.
// database connection
var dbConn = require('./lib/db');If you run the project (npm start) and everything is fine, you’ll see the connection successful message.
Step 3 : Create Product Model
In the root folder, make a directory named ‘models‘. Under models, create a file called ‘product.js‘. This is the product model. Let’s define the products table schema.
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const Schema = mongoose.Schema;
let ProductSchema = new Schema({
name: {type: String, required: true, max: 100},
price: {type: Number, required: true},
});
// Export the model
module.exports = mongoose.model('Product', ProductSchema);Step 4 : Create Product Controller
Again in the root directory of the project create a folder named ‘controllers‘. Under controllers folder, make a file called ‘product.js‘. We will write make create, read, update and delete product methods in this controller.
Open the newly created product controller and paste this code:
// include product model
const Product = require('../models/product');
// create a new Product.
exports.product_create = function (req, res) {
// validate request
if(!req.body.name || !req.body.price) {
return res.status(400).send({
success: false,
message: "Please enter product name and price"
});
}
// create a product
let product = new Product(
{
name: req.body.name,
price: req.body.price
}
);
// save product in the database.
product.save()
.then(data => {
res.send({
success: true,
message: 'Product successfully created',
data: data
});
}).catch(err => {
res.status(500).send({
success: false,
message: err.message || "Some error occurred while creating the product."
});
});
};
// retrieve and return all products.
exports.all_products = (req, res) => {
Product.find()
.then(data => {
var message = "";
if (data === undefined || data.length == 0) message = "No product found!";
else message = 'Products successfully retrieved';
res.send({
success: true,
message: message,
data: data
});
}).catch(err => {
res.status(500).send({
success: false,
message: err.message || "Some error occurred while retrieving products."
});
});
};
// find a single product with a id.
exports.product_details = (req, res) => {
Product.findById(req.params.id)
.then(data => {
if(!data) {
return res.status(404).send({
success: false,
message: "Product not found with id " + req.params.id
});
}
res.send({
success: true,
message: 'Product successfully retrieved',
data: data
});
}).catch(err => {
if(err.kind === 'ObjectId') {
return res.status(404).send({
success: false,
message: "Product not found with id " + req.params.id
});
}
return res.status(500).send({
success: false,
message: "Error retrieving product with id " + req.params.id
});
});
};
// update a product by the id.
exports.product_update = (req, res) => {
// validate request
if(!req.body.name || !req.body.price) {
return res.status(400).send({
success: false,
message: "Please enter product name and price"
});
}
// find product and update
Product.findByIdAndUpdate(req.params.id, {
$set: req.body
}, {new: true})
.then(data => {
if(!data) {
return res.status(404).send({
success: false,
message: "Product not found with id " + req.params.id
});
}
res.send({
success: true,
data: data
});
}).catch(err => {
if(err.kind === 'ObjectId') {
return res.status(404).send({
success: false,
message: "Product not found with id " + req.params.id
});
}
return res.status(500).send({
success: false,
message: "Error updating product with id " + req.params.id
});
});
};
// delete a product with the specified id.
exports.product_delete = (req, res) => {
Product.findByIdAndRemove(req.params.id)
.then(data => {
if (!data) {
return res.status(404).send({
success: false,
message: "Product not found with id " + req.params.id
});
}
res.send({
success: true,
message: "Product successfully deleted!"
});
}).catch(err => {
if (err.kind === 'ObjectId' || err.name === 'NotFound') {
return res.status(404).send({
success: false,
message: "Product not found with id " + req.params.id
});
}
return res.status(500).send({
success: false,
message: "Could not delete product with id " + req.params.id
});
});
};In this controller, I’ve created the CRUD functions.
Step 5 : Register Product Routes
In this step, we will register routes to connect to the product controller’s methods.
Go to the routes folder and make a file named ‘products.js‘. Then paste this code:
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
// include product controller
const product_controller = require('../controllers/product');
// routes
router.get('/', product_controller.all_products);
router.post('/create', product_controller.product_create);
router.get('/:id', product_controller.product_details);
router.put('/update/:id', product_controller.product_update);
router.delete('/delete/:id', product_controller.product_delete);
module.exports = router;We’ve defined all product CRUD routes. Let’s import the product routes to app.js. After that, the routes will work.
var productsRouter = require('./routes/products');
app.use('/products', productsRouter);Done. Our project is ready to run…! ?
Step 6 : The Overview
The final app.js looks like:
var createError = require('http-errors');
var express = require('express');
var path = require('path');
var cookieParser = require('cookie-parser');
var logger = require('morgan');
// database connection
var dbConn = require('./lib/db');
var indexRouter = require('./routes/index');
var usersRouter = require('./routes/users');
var productsRouter = require('./routes/products');
var app = express();
// view engine setup
app.set('views', path.join(__dirname, 'views'));
app.set('view engine', 'ejs');
app.use(logger('dev'));
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.use(cookieParser());
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')));
app.use('/', indexRouter);
app.use('/users', usersRouter);
app.use('/products', productsRouter);
// catch 404 and forward to error handler
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
next(createError(404));
});
// error handler
app.use(function(err, req, res, next) {
// set locals, only providing error in development
res.locals.message = err.message;
res.locals.error = req.app.get('env') === 'development' ? err : {};
// render the error page
res.status(err.status || 500);
res.render('error');
});
module.exports = app;The package.json file looks like:
{
"name": "nodejs-api-crud-mongodb",
"version": "0.0.0",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"start": "node ./bin/www"
},
"dependencies": {
"cookie-parser": "~1.4.4",
"debug": "~2.6.9",
"ejs": "~2.6.1",
"express": "~4.16.1",
"http-errors": "~1.6.3",
"mongoose": "^5.7.4",
"morgan": "~1.9.1"
}
}
Step 7 : Run and See Output
We’ve finished all the tasks. Let run the project using this command:
npm startOur project will be run on port 3000 and the localhost URL looks like: http://localhost:3000. If you visit this link, you’ll see a message like ‘ Welcome to Express’.
Now let’s test the APIs using Postman application.
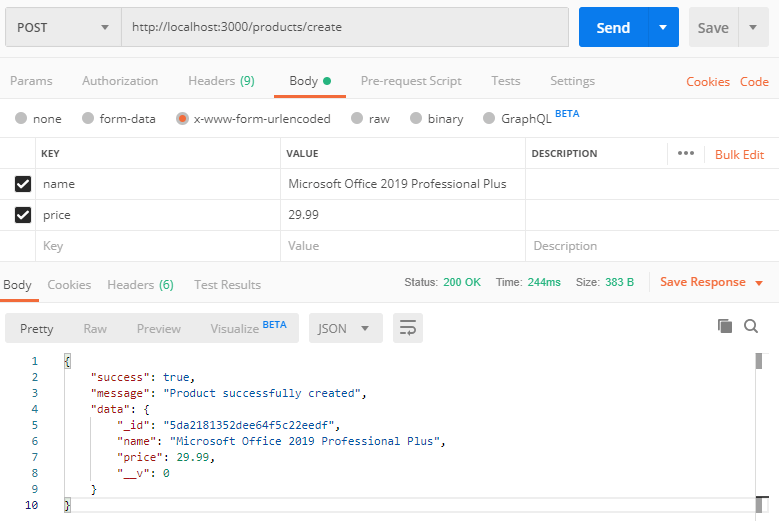
Create a Product API: http://localhost:3000/products/create
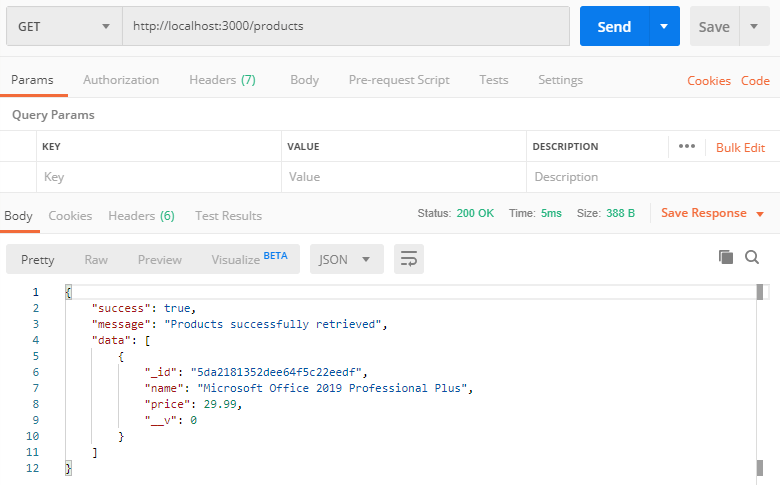
Retrieve all Products API: http://localhost:3000/products
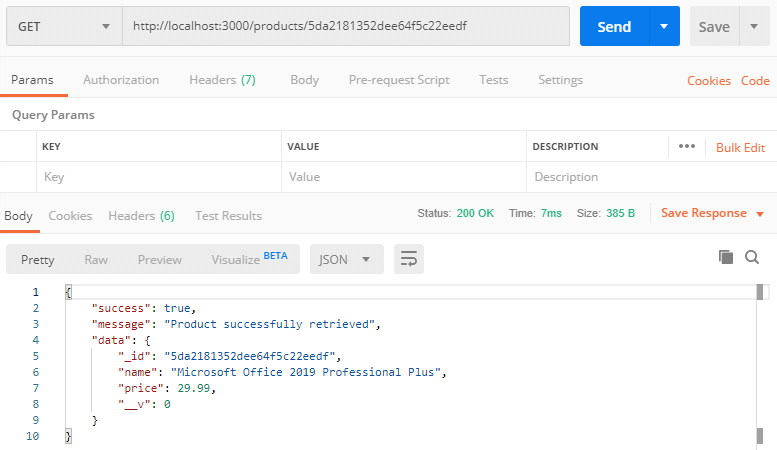
Retrieve Single Product API: http://localhost:3000/products/:id
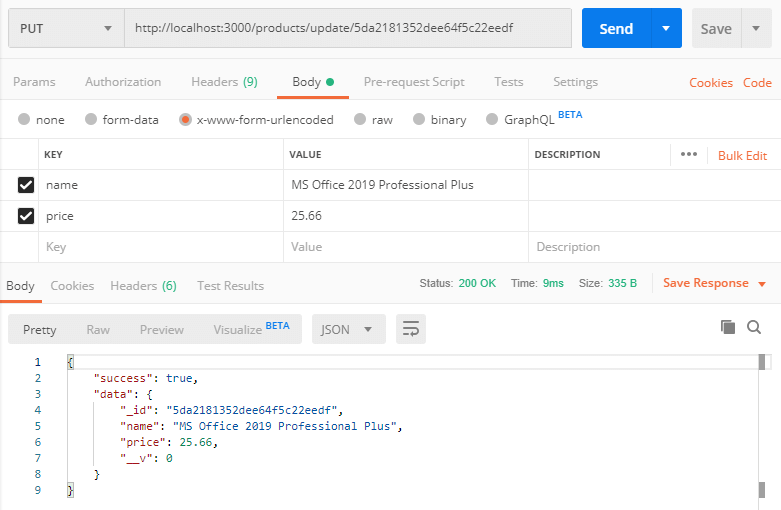
Update Product API: http://localhost:3000/products/update/:id
Delete Product API: http://localhost:3000/products/delete/:id
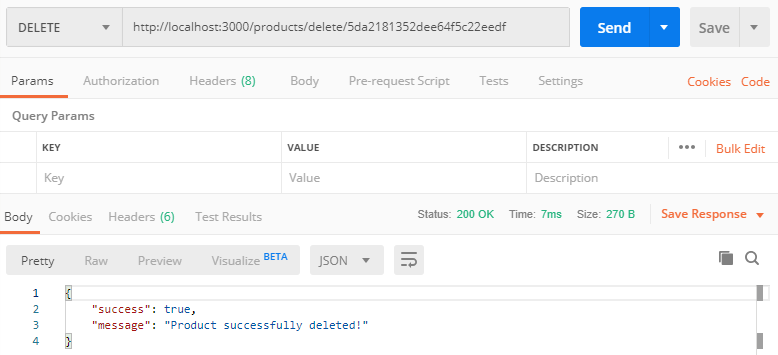
The tutorial is over. You can download this project from GitHub. Thank you.
Md Obydullah
Software Engineer | Ethical Hacker & Cybersecurity...
Md Obydullah is a software engineer and full stack developer specialist at Laravel, Django, Vue.js, Node.js, Android, Linux Server, and Ethichal Hacking.